Health consciousness requires us to be aware of the common diseases in our environment and how they are contracted, spread and cured. There are two types of diseases, communicable and non-communicable diseases.
Communicable diseases are also called infectious diseases or transmissible diseases. They are illnesses that result from the infection, presence, and growth of pathogenic agents in individuals. These pathogenic agents include viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and helminths. Communicable diseases that are well known in our society include malaria, typhoid fever, pneumonia, tuberculosis, Ebola, HIV/AIDS, rabies, tetanus, worm infestation, and gastroenteritis.
These diseases can be controlled and are avoidable by taking care of the vectors, carrying out good hygiene, healthy feeding and maintain a proper social life. When infected, prompt treatment of the infected also helps both to cure the victims and to prevent it’s spread. Communicable diseases are the major killer diseases in Nigeria. We can control them if we desire.
Non-communicable diseases are diseases that are not transmissible directly from one person to another. Factors responsible for these diseases may be age, race, lifestyle etc. Some of them include Parkinson’s disease, autoimmune diseases, stroke, most heart diseases, cancers, diabetes, kidney diseases, cataracts, Alzheimer’s disease and many more.
Heart Disease
- Heart disease is a general term that describes many heart conditions.
- It is also a major risk factor for stroke
- Coronary artery disease is the most common. It occurs when coronary (heart) arteries form clots. This block or narrows the vessels thereby preventing oxygen and nutrient from reaching the heart muscles.
- Angina is chest pain resulting from infarcted heart muscle. It is also called heart attack.
There are several risk factors to take note of that cause heart diseases. Some of them we can control while some we cannot control. Some of the factors we cannot control include:
- Age: As we get older our risk of heart disease increases
- Gender: Males over the age of 55 years and females after menopause has been reached.
- Family History: The risk increases if any member of the family had heart disease in the past.
- Race: Blacks tend to have higher risk than whites.
Risk factors we can control include the following:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High blood sugar /diabetes
- High blood fat (cholesterol)
- Smoking
- Being overweight
- Physical inactivity
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress
Stroke
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is cut off. Without oxygen and nutrient-rich blood, brain cells begin to die. If the blood supply is not restored, the affected part of the brain dies, causing disability and/or even death. Risk factors are the same as for heart disease. Keep in mind that the more risk factors a person has for stroke the greater the risk.
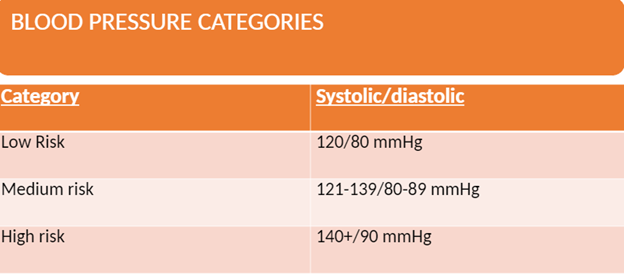
High Blood Pressure
This is also known as hypertension. It occurs when the force of blood pushing against arterial walls as blood is pumped out of the heart is excessively high. Hypertension is the number one risk factor for stroke and major risk factor for heart disease, which should not be neglected.

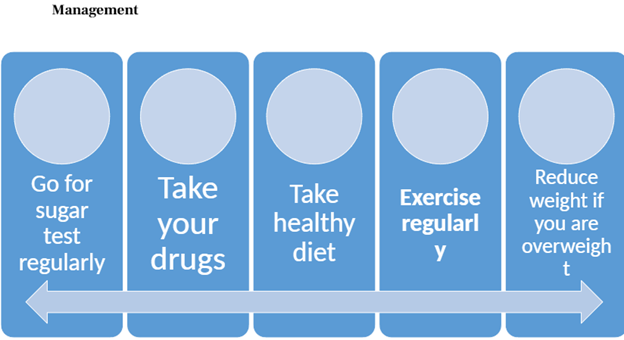
We can lower the risk factors for hypertension through our lifestyle choices including the following:
- Having regular BP check and immediate action taken when necessary.
- Reducing your salt intake.
- Reducing the consumption of alcoholic drinks.
- Controlling stress by setting aside some time every day to relax.
- Stop smoking.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Staying physically active.
High Blood Cholesterol
Cholesterol is the free fat found in the blood stream. It is used by the body to make cell membranes. Sources of dietary cholesterol include meat, milk, dairy, sea food, hydrogenated/refined vegetable oil and egg yolk There are three types of blood fats:
- Low density Lipo-protein cholesterol (LDL) – also known as bad cholesterol. They promote the build up of fatty plaque on the walls of artery making them narrower. The increase in LDL cholesterol narrows the arteries thereby increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- High density Lipo-protein cholesterol (HDL) – also known as good cholesterol. HDL helps in chewing the plaques in the artery. We need to have more HDL for good health.
- Triglyceride – fats carried in the blood from the food we eat. High triglycerides are harmful. It is common in female, people that take alcohol and diabetic patients.
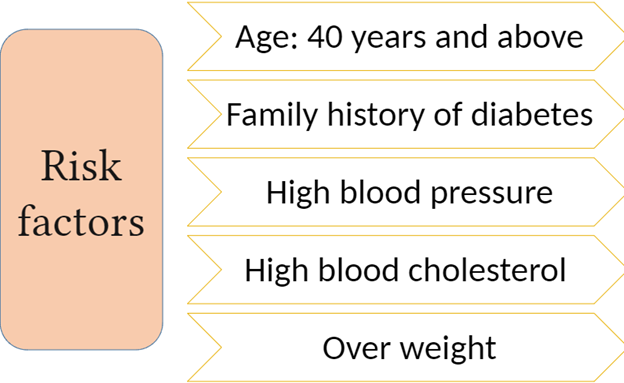
It is advisable to regularly check your cholesterol levels especially if you have the risk factors. Risk factors to keep in mind include:
- Male over 40 years
- Female over 50 years and postmenopausal
- Previous history of stroke or heart disease
- Overweight
- Family history of heart disease or stroke
To promote good health, it is encouraged to reduce dietary cholesterol intake which can be achieved through the following ways:
- Avoid trans-fat which are frequently found in foods made with shortening or partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, hard margarine, fast foods, and many prepared foods. Trans fats raise bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol.
- Choose low-fat milk
- Eat more whole grains, cereals, fruits, and vegetable
- For Snacks: Avoid junk food
- Use low-fat cooking methods such as baking, boiling, or steaming instead of frying the food
- Stop smoking. Smoking increases LDL
- Get physically active to increase HDL
- Take your drugs when necessary
Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition that develops when the body does not produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. The blood sugar is then raised. It increases the risk of high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease and stroke.
Diabetes are of three types:
- TYPE I:
- It develops in children, teenagers, young adults and even people in their 30s.
- It occurs when the pancreas no longer produces insulin which is needed to convert sugar to energy.
- This makes up 10{53e0e43491e6ac3b300e64b98347cc2563bcc73f8d91f69977895bc6a60e7c33} of diabetics.
- TYPE II:
- It occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body does not use the insulin that is produced.
- It is also called adult-onset or non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Ninety per cent of people with diabetes have type 2.
- It is common among overweight people and can be controlled by good diet and weight reduction.
- TYPE III:
- It is called gestational diabetes.
- Here, sugar level rises during pregnancy but disappears after the birth of the baby.
- The patient or the baby may develop diabetes later in life.
- It makes up about 2-4{53e0e43491e6ac3b300e64b98347cc2563bcc73f8d91f69977895bc6a60e7c33} of diabetics.